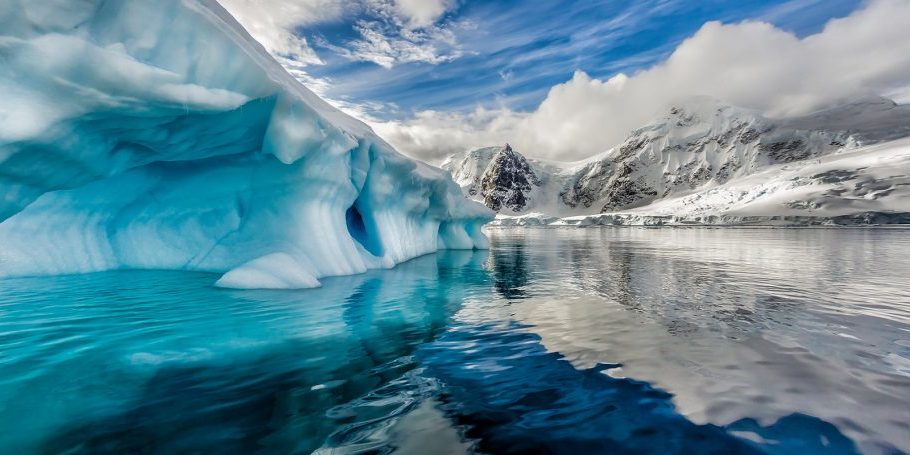
Antarctica, the Earth’s last great wilderness, faces an uncertain future. As the world grapples with climate change, resource demands, and international politics, the frozen continent stands at a crossroads. Preserving Antarctica’s pristine environment and its role in global systems requires bold action and collective responsibility. Find out more here about the future of Antarctica.
Climate Change: A Looming Threat
The impact of climate change on Antarctica is already evident. Rising global temperatures are accelerating the melting of ice sheets and glaciers. This process contributes significantly to global sea-level rise. Scientists estimate that if all Antarctic ice were to melt, sea levels would rise by about 58 meters, inundating coastal cities worldwide.
The West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) is particularly vulnerable. Warm ocean currents are eroding its base, leading to faster ice loss. The melting of the Thwaites Glacier, often called the “Doomsday Glacier,” poses a significant risk. Its destabilization could trigger the collapse of adjacent ice sheets, compounding the effects on sea levels.
Addressing climate change requires urgent action. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to sustainable energy sources are critical steps. Antarctica’s fate is directly tied to the global effort to combat climate change.
The Role of International Cooperation
Antarctica is governed by the Antarctic Treaty System, which designates the continent as a zone of peace and scientific research. The treaty, signed in 1959, remains a model for international collaboration. However, its provisions face challenges as geopolitical interests evolve.
Key treaty provisions, including the ban on mineral exploitation, are set for review in 2048. The outcome of these discussions will shape Antarctica’s future. Ensuring the treaty’s integrity requires diplomatic efforts to balance conservation with scientific and economic interests.
Emerging powers, such as China and India, have increased their presence in Antarctica. While their investments in research are welcomed, concerns about their long-term intentions persist. Maintaining Antarctica as a neutral and peaceful region will depend on transparency and cooperation among nations.
The Potential for Resource Exploitation
Antarctica’s vast resources remain a point of contention. Beneath its ice lie untapped reserves of oil, gas, and minerals. Advances in technology could make resource extraction feasible in the coming decades. However, such activities would come at a high environmental cost.
The Protocol on Environmental Protection, an extension of the Antarctic Treaty, prohibits mineral resource activities. Preserving this prohibition is essential to safeguarding Antarctica’s ecosystems. Exploiting these resources could disrupt fragile habitats and exacerbate global environmental issues.
Scientific Discoveries and Opportunities
Antarctica’s unique environment offers unparalleled opportunities for scientific research. The continent’s ice cores provide a record of Earth’s climate history, helping scientists understand past and future climate trends. Subglacial lakes, such as Lake Vostok, may harbor ancient microbial life, offering insights into evolution and potential extraterrestrial ecosystems.
Astronomical research also benefits from Antarctica’s clear skies and minimal light pollution. Telescopes located here contribute to discoveries about the universe’s origins and structure. Continued investment in Antarctic science is crucial for advancing human knowledge.
Tourism and Human Impact
Tourism in Antarctica has grown significantly in recent years. Visitors are drawn to its untouched landscapes and unique wildlife. While tourism raises awareness about Antarctica’s importance, it also presents challenges.
Human activity increases the risk of pollution and disturbance to delicate ecosystems. Strict regulations govern Antarctic tourism, but ensuring compliance remains a challenge. Sustainable tourism practices are essential to minimize its environmental footprint.
Technological Innovations and Preservation
Advances in technology play a vital role in Antarctica’s future. Autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), satellite imaging, and drones enable researchers to study the continent with minimal environmental disruption. These tools provide valuable data on ice movement, ecosystems, and geological features.
Technology also supports conservation efforts. Renewable energy installations at research stations reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Innovations in waste management help protect Antarctica’s pristine environment.
Challenges Ahead
The future of Antarctica depends on addressing several pressing challenges:
- Climate Change: Accelerating ice loss demands global action to reduce emissions and adapt to rising sea levels.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Balancing national interests with the principles of the Antarctic Treaty requires continued diplomacy.
- Resource Protection: Maintaining the ban on mineral exploitation is essential for preserving Antarctica’s ecosystems.
- Sustainable Tourism: Managing human impact while fostering appreciation for the continent’s importance is a delicate balance.
- Scientific Collaboration: Expanding international research efforts can unlock new discoveries and strengthen global cooperation.
Conclusion
Antarctica’s future is inextricably linked to the global community’s choices and actions. As a symbol of international cooperation and environmental stewardship, the continent challenges humanity to rise above narrow interests and prioritize the greater good. Protecting Antarctica requires a commitment to science, conservation, and collaboration. The decisions made today will determine whether this icy frontier remains a beacon of hope for future generations or a testament to missed opportunities. Find out more here about the future of Antarctica. Read more articles on this Antarctica blog by Daniel River.