Antarctica and Chile share a unique and enduring relationship shaped by geography, exploration, and science. Chile, as one of the closest nations to Antarctica, has a significant historical and strategic interest in the frozen continent. This connection spans centuries, rooted in both cultural ties and scientific endeavors. Understanding this history reveals the depth of Chile’s commitment to preserving and studying Antarctica. Chile and Antarctica are near to each other. Here is more information on how Antarctica and Chile have a long history.
Geographic Proximity and Strategic Importance
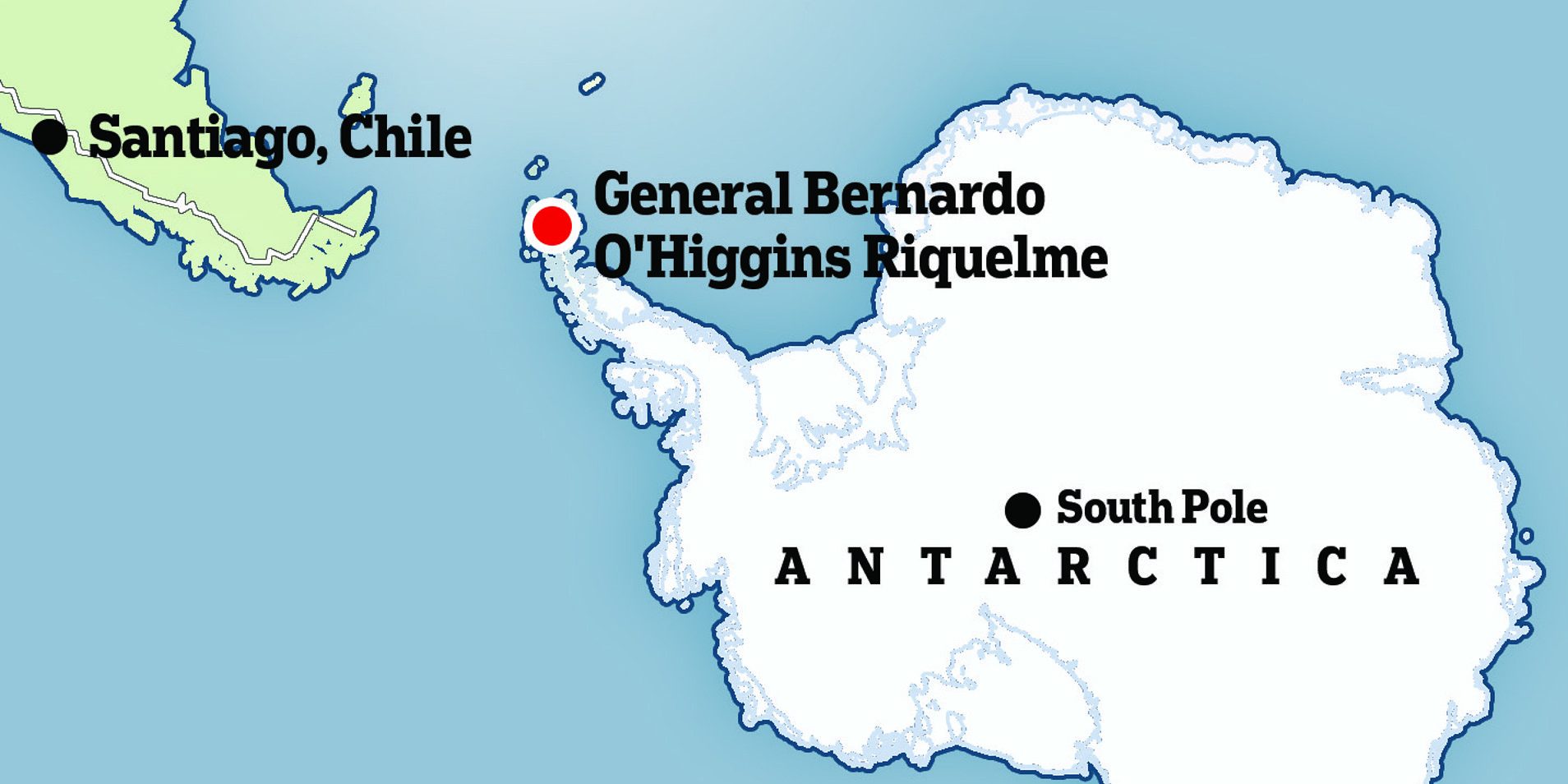
Chile’s geographic position makes it a gateway to Antarctica. The southernmost tip of Chile, particularly Punta Arenas, serves as a key launch point for expeditions to the continent. The distance between Punta Arenas and Antarctica is approximately 1,000 kilometers, making it one of the shortest routes to the icy land.
This proximity gives Chile strategic advantages. It has facilitated Chile’s role as a logistical hub for Antarctic research and tourism. The city of Punta Arenas hosts international research teams and supplies expeditions heading south. This geographic connection also underpins Chile’s historical claim to parts of Antarctica.
Early Exploration and Claims
Chile’s interest in Antarctica dates back to the 19th century. Chilean sailors and fishermen were among the earliest explorers to venture into Antarctic waters. These early interactions laid the groundwork for Chile’s presence in the region.
In 1940, Chile formally asserted a territorial claim to a portion of Antarctica, known as the Chilean Antarctic Territory. This area overlaps with claims made by Argentina and the United Kingdom. While the Antarctic Treaty of 1959 suspended all territorial claims, it recognized the historical interests of claimant nations like Chile.
The Role of the Antarctic Treaty
Chile played a crucial role in the development of the Antarctic Treaty System. The treaty, signed in 1959, established Antarctica as a zone of peace and scientific research. It prohibits military activity, mineral exploitation, and nuclear testing while promoting international cooperation.
As one of the original signatories, Chile remains committed to the treaty’s principles. The nation actively participates in Antarctic governance and conservation efforts. This involvement underscores Chile’s long-standing dedication to preserving the continent’s unique environment.
Scientific Research and Collaboration
Scientific research forms a cornerstone of Chile’s relationship with Antarctica. The nation operates several research stations on the continent, including the Escudero and O’Higgins bases. These facilities focus on diverse fields such as climate science, glaciology, and marine biology.
Chile’s research contributes to global understanding of Antarctica’s role in Earth’s climate system. For instance, studies on ice sheet dynamics and ocean currents have implications for predicting sea-level rise. Collaboration with international teams enhances the scope and impact of Chilean research.
The Chilean Antarctic Institute (INACH) oversees the nation’s scientific activities in Antarctica. It coordinates research projects, logistical support, and educational initiatives. INACH also fosters partnerships with universities and global organizations, reinforcing Chile’s role in Antarctic science.
Cultural and Educational Ties
Chile’s connection to Antarctica extends beyond science. The nation has integrated Antarctic themes into its cultural and educational frameworks. Museums, such as the Nao Victoria Museum in Punta Arenas, showcase artifacts and exhibits related to Antarctic exploration.
Educational programs aim to raise awareness about Antarctica’s importance. Schools include Antarctic studies in their curricula, fostering a sense of connection among young Chileans. Public events and lectures further promote understanding of the continent’s role in global ecosystems.
Tourism and Economic Impact
Antarctic tourism has become a growing industry, with Chile playing a pivotal role. Punta Arenas serves as a departure point for cruises and flights to Antarctica. These tours offer visitors a chance to experience the continent’s pristine landscapes and unique wildlife.
While tourism brings economic benefits, it also poses challenges. Chile actively promotes responsible tourism practices to minimize environmental impact. Strict regulations and guidelines ensure that human activities do not harm Antarctica’s fragile ecosystems.
Climate Change and Environmental Stewardship
Antarctica’s changing environment highlights the importance of Chile’s stewardship. Rising temperatures and melting ice threaten the continent’s ecosystems. Chilean researchers are at the forefront of studying these changes and their global implications.
Chile’s commitment to environmental protection extends to its Antarctic policies. The nation advocates for sustainable practices and international cooperation. Initiatives like marine protected areas aim to safeguard Antarctic biodiversity for future generations.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
Chile faces several challenges in maintaining its Antarctic presence. Climate change, logistical complexities, and competition for resources require innovative solutions. However, these challenges also present opportunities for growth and collaboration.
Advances in technology can enhance Chile’s research capabilities. Drones, satellite imaging, and autonomous vehicles enable more detailed studies of Antarctica’s landscapes and ecosystems. Strengthening partnerships with other nations can further expand Chile’s role in Antarctic governance and science.
Conclusion
Chile’s long history with Antarctica reflects a deep commitment to the continent’s preservation and study. From early exploration to modern scientific research, Chile has played a vital role in shaping the understanding of this frozen frontier. The nation’s proximity, cultural ties, and strategic interests ensure that its connection to Antarctica remains strong.
As the challenges of climate change and environmental protection grow, Chile’s leadership will be crucial. By fostering collaboration and innovation, Chile can continue to contribute to the conservation of Antarctica. This enduring relationship not only benefits Chile but also supports global efforts to safeguard one of Earth’s most remarkable regions. Chile and Antarctica are near to each other. Here is more information on how Antarctica and Chile have a long history.